AI tools are powerful, but without domain-specific knowledge, they often produce irrelevant or inaccurate results. This happens because generic AI relies on broad data, leading to errors like hallucinations (making up false information) or generic outputs that fail to address specific needs. For startups, this can waste time, erode trust, and even harm user relationships.
To make AI outputs reliable and relevant, startups must:
- Embed domain-specific knowledge: Train AI on specialized data relevant to your industry.
- Use tools like RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation): Connect AI to real-time, accurate external data sources.
- Involve domain experts: Validate outputs and refine AI systems with expert input.
- Test rigorously: Ensure accuracy through benchmarks, human audits, and feedback loops.
The key takeaway? AI needs structured context – like internal documents, industry rules, and real-time updates – to deliver actionable, trustworthy outputs. Without this, even advanced AI systems risk producing errors that can derail projects and damage trust.
Make your LLM app a Domain Expert: How to Build an Expert System – Christopher Lovejoy, Anterior
The Problem: When AI Produces Wrong or Useless Results
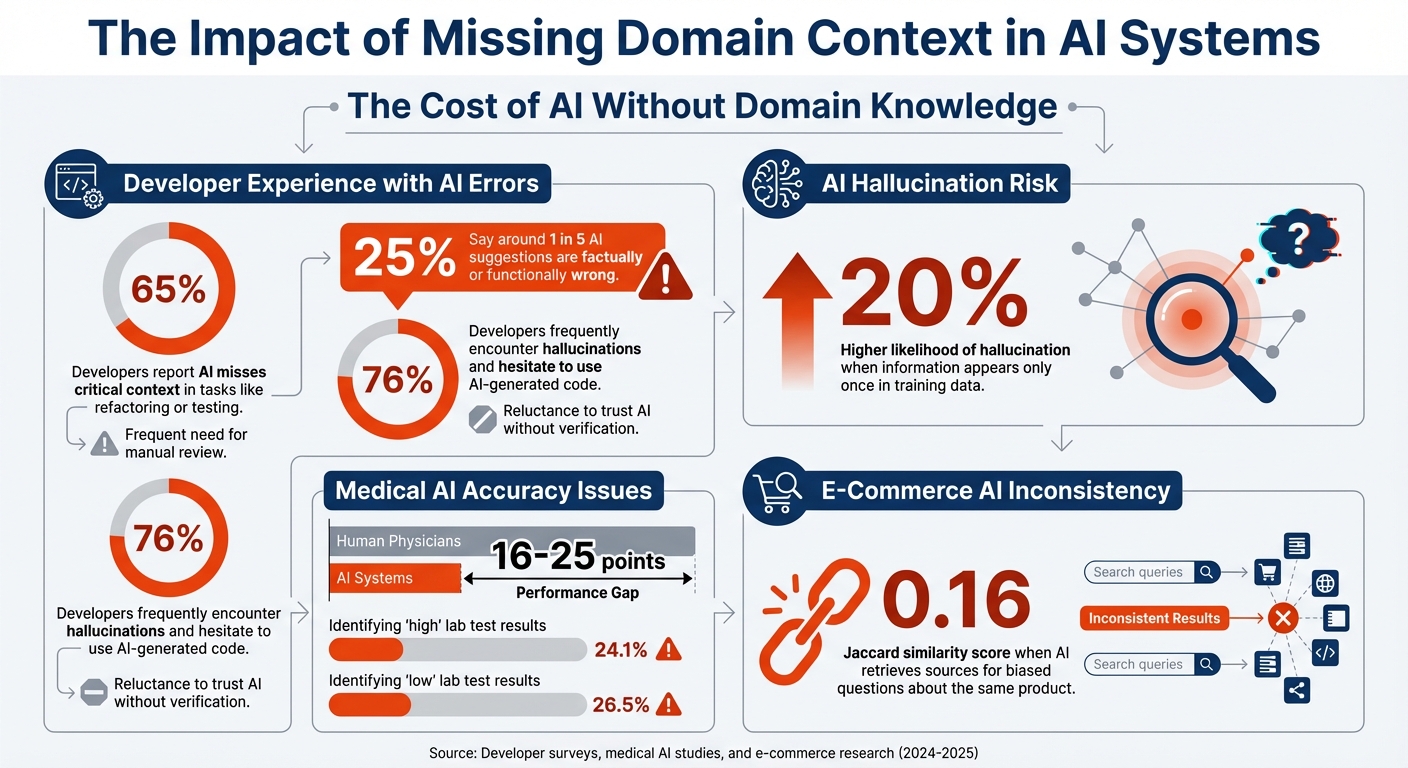
The Impact of Missing Domain Context in AI Systems: Key Statistics
When AI systems lack the proper domain knowledge, they often stumble, leading to wasted resources and damaged trust. The problem arises in two ways: either the AI fabricates information that seems correct but isn’t, or it churns out generic responses that fail to address specific business challenges. Both scenarios waste time and undermine confidence in your product long before users even interact with it.
AI systems rely heavily on the context available in their "working memory." If that context is incomplete or outdated, the results are often incorrect or overly generalized. For instance, 65% of developers report that AI misses critical context during tasks like refactoring or testing, and 25% say around 1 in 5 AI suggestions are factually or functionally wrong [5]. These errors can range from made-up details to irrelevant responses, both of which can slow down progress on your minimum viable product (MVP).
AI Hallucinations: When AI Makes Things Up
AI hallucinations occur when the system confidently generates statements that are entirely false. This isn’t just a small bug – it’s a direct result of how these systems are designed. If a piece of information appears only once in the training data, the AI is 20% more likely to hallucinate related details [8]. With no consistent patterns to rely on, the system fills in gaps with what it “thinks” might be true.
Take the case of a Bosch Smart Home AI chatbot in January 2026. It provided a user with detailed instructions on integrating a TP-Link smart plug into the Bosch system. The AI described navigating to a "Third-Party Integrations" menu and following specific steps. The issue? That menu didn’t exist. The AI had stitched together patterns from unrelated systems to fabricate a process that sounded plausible but was entirely false [4]. For startups, such blunders can delay development and erode trust with early adopters.
"The absence of an abstention mechanism turns epistemic uncertainty into linguistic certainty." – Moritz Hain, Marketing Coordinator, Sapien [8]
AI systems are built to always provide an answer, even when they lack the data to do so accurately. They don’t have a mechanism to say, “I don’t know.” This leads to what researchers call the calibration paradox, where low-confidence situations result in high-confidence falsehoods [8]. According to recent data, 76% of developers frequently encounter hallucinations and are hesitant to use AI-generated code without manual review [5]. While hallucinations create outright falsehoods, even correct outputs can fall short if they lack proper context.
Generic Outputs That Miss the Mark
Even when AI avoids hallucinating, it often delivers outputs that are technically correct but practically useless. Without domain-specific knowledge, the system defaults to generic, one-size-fits-all answers that don’t align with your business needs. This happens when AI has surface-level knowledge about many things but no deep understanding of your specific challenges [1].
For example, imagine a customer support chatbot designed to reduce service requests. If it doesn’t understand your product’s unique features or troubleshooting steps, it might respond to a technical question with, “Please call technical support.” While accurate, this advice completely misses the point of having an automated system in the first place [6]. Such responses frustrate users and undermine the strategic value of integrating AI.
This lack of precision can disrupt multi-step processes. An AI agent might handle individual tasks correctly but fail to see the bigger picture. For instance, a startup building an internal employee directory might ask the AI to find details about “Mike Jordan” on the team. Without the right context, the AI might return information about the basketball legend instead of the specific employee [7]. While technically accurate, the output is irrelevant and unhelpful.
Similarly, AI-generated code can create more problems than it solves. Quick fixes often lead to brittle code, security risks like SQL injection vulnerabilities, and mounting technical debt [5]. While the initial output might look functional, it often collapses under real-world conditions due to a lack of alignment with your domain’s unique requirements and constraints.
Examples: What Happens When AI Lacks Domain Knowledge
When AI operates without domain-specific understanding, the results can be not only disappointing but also harmful. From healthcare to retail, documented failures reveal how the absence of contextual knowledge leads to dangerous recommendations, wasted resources, and a loss of trust.
Healthcare AI That Misread Medical Data
Take IBM’s Watson for Oncology as an example. This system was designed to assist oncologists but fell short in a critical way – it provided unsafe and incorrect treatment recommendations. Why? It was trained using synthetic, hypothetical cases rather than real-world patient data and clinical guidelines [9]. Without the practical reasoning that experienced oncologists bring to the table, the system risked making recommendations that could harm patients instead of helping them.
Another study highlights how AI models can falter when applied to real medical scenarios. Researchers tested leading AI models on 2,400 real patient cases from the MIMIC-IV database (2024–2025). The results were concerning: the Meditron (70B) model misdiagnosed cholecystitis as "gallstones", entirely missing key inflammatory markers. Worse, the models failed to order essential pancreatic enzyme tests for pancreatitis cases, ignoring basic diagnostic protocols. The performance gap between these AI systems and human physicians ranged from 16 to 25 points [12]. When tasked with interpreting lab results, some advanced models achieved only 24.1% accuracy in identifying "high" test results and 26.5% for "low" results [12].
"Large language models often encode cognitive biases and display sycophantic behavior, distorting responses and unpredictably influencing the clinicians who prompt them."
- Michelle M. Li et al., Harvard Medical School [11]
E-Commerce Recommendations That Drove Customers Away
While errors in retail AI may not endanger lives, they can still cause serious damage to a business’s reputation and bottom line. A February 2025 study examined how retrieval-augmented AI systems handle customer queries about products and services. The findings were troubling: when researchers asked biased questions like "Why is this safe?" versus "Why is this dangerous?" about the same product, the AI systems retrieved vastly different supporting materials. The overlap between sources was minimal, with a Jaccard similarity score of only 0.16 [10].
Such inconsistencies can erode customer trust. For example, recommendation engines that fail to address underlying customer concerns or overpromise benefits often leave shoppers dissatisfied. These systems tend to interpret queries too literally, missing the nuances that industry experts use to evaluate relevance [10] [3]. Without the necessary domain knowledge, AI struggles to differentiate between what is technically accurate and what is genuinely helpful for specific business goals.
These examples emphasize a crucial point: AI systems must be equipped with domain expertise before being scaled for real-world applications. Without it, their potential to mislead or underperform becomes a serious liability.
How to Build Domain Knowledge Into Your AI Systems
AI systems lacking domain expertise can become more of a problem than a solution. For startups, embedding specialized knowledge directly into these systems is essential. By focusing on the need for industry-specific insights, you can ensure your AI evolves into a reliable and precise tool.
Context Engineering: Embedding Expertise Into AI
The days of relying solely on generic prompt tuning are fading. A newer approach, called Context Engineering, focuses on designing the complete information environment that an AI accesses [13][14]. To build your AI’s minimum viable product (MVP), consider a three-tiered context structure:
- The persistent layer defines the AI’s core identity, roles, and organizational guidelines.
- The time-sensitive layer updates the AI with the latest information using tools like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) or APIs at the time of each request.
- The transient layer manages short-term memory, such as recent user interactions [13].
"The era of the Prompt Engineer is over. In its place, a more robust, scalable, and essential discipline has emerged: Context Engineering." – ALFAZA [14]
For a simple starting point, use a basic context stack: a document repository, a user context store, and an orchestration script [13]. Another effective tool is a "verified semantic cache", a curated database of expert-approved answers to common questions [1]. To avoid the "lost-in-the-middle" effect – where models overlook details buried in lengthy prompts – place critical domain instructions upfront and user-specific data at the end [1].
This structured approach naturally highlights the importance of involving industry experts to validate and refine the system’s outputs.
Working with Industry Experts
Assigning a Principal Domain Expert as the Directly Responsible Individual (DRI) can streamline decision-making on AI accuracy, avoiding the inefficiencies of committee-based consensus [15]. When hiring, look for experts who have experience reviewing AI outputs – they’re better equipped to spot subtle inaccuracies or hallucinations [15].
These experts are instrumental in defining a comprehensive error classification system, outlining all potential ways the AI might produce incorrect results [15]. Their reviews also help fine-tune "retrieval weights" in RAG systems, improving responses without the complexity of full model retraining [2]. As your team of reviewers grows, use statistical measures like inter-reviewer kappas to maintain consistency and quality across evaluations [15].
Once the system is set up with expert guidance, continuous feedback loops ensure ongoing improvement.
Using Feedback Loops to Improve AI Over Time
Feedback loops are essential for adapting AI systems to changing industry trends and user needs. By analyzing AI outputs and user interactions, these loops help retrain models over time, reducing errors and improving relevance [16].
C3 AI offers practical examples of this approach. In their Reliability application, maintenance operators receive AI-generated risk scores to prioritize tasks. If an operator disagrees with a recommendation, they log their decision, which updates the model and improves future predictions [16]. Similarly, their Anti-Money-Laundering application incorporates real-world outcomes into its system, adapting to new criminal patterns as they emerge [16].
"A feedback loop (also known as closed-loop learning) describes the process of leveraging the output of an AI system and corresponding end-user actions in order to retrain and improve models over time." – C3 AI [16]
To gather high-quality data, combine implicit feedback (like click patterns and acceptance rates) with explicit feedback (such as asking users directly if their query was fully answered) [17]. Use "champion/challenger" testing to compare new models against existing ones in real-world scenarios before rolling them out [16]. Allowing users to edit or annotate AI outputs also generates valuable training data, helping fine-tune the system to meet specific industry standards [17].
sbb-itb-51b9a02
AlterSquare‘s I.D.E.A.L. Framework for Context-Aware AI
Creating AI systems that understand and respond to domain-specific needs requires a structured approach. AlterSquare’s I.D.E.A.L. Framework offers startups a streamlined method to develop AI-powered MVPs that are both accurate and ready for the market. Designed to compress traditional development timelines from months or years into a 30-day process, this framework helps startups capitalize on market opportunities while gathering valuable early feedback [18].
It’s a blend of strategic planning and rapid execution, tailored for speed and precision.
The 5 Phases of I.D.E.A.L.
The framework is broken into five distinct phases, each designed to ensure the AI system is grounded in domain-specific context:
- Identify: This phase focuses on defining the problem and understanding the target audience. Through detailed buyer personas and user interviews, startups can ensure the AI tackles real pain points instead of relying on assumptions [18].
- Design: Here, core features are mapped out, and the right AI tools are selected. Technical requirements, including data sources, processing methods, and system architecture, are outlined to ensure a clear development path [18].
- Execute: The MVP is built using agile mini-sprints, prioritizing only the most essential features. Monitoring tools are also implemented to track how the AI performs in real-world scenarios [18].
- Assess: Beta testers – typically 5 to 10 – are recruited to perform specific tasks. Their feedback helps validate the AI’s domain accuracy and identify usability issues before a broader launch [18].
- Learn: After launch, analytics and user feedback drive continuous optimization. This phase ensures the AI evolves to meet changing user needs [18][19].
"AI’s integration into MVP development not only speeds up the process but also enhances the accuracy of decisions, leading to more successful and adaptable products." – AlterSquare [19]
How I.D.E.A.L. Helps Startups Build Better MVPs
The I.D.E.A.L. Framework delivers measurable benefits by embedding domain expertise directly into the development process. Startups that adopt this structured approach achieve product-market fit 4x faster than those simply adding AI to existing products. Data shows that 47% of AI-native companies reach scale quickly, compared to only 13% of non-native firms [20].
One of the framework’s strengths lies in its focus on feature prioritization. Using a priority matrix, startups concentrate on core functionalities, avoiding "feature creep" and aligning development with business goals [18][21]. By leveraging first-party user data, second-party partnerships, and third-party market insights, startups create AI products that adapt based on actual user behavior instead of assumptions [18].
The framework also delivers clear cost and time advantages. AI-assisted development can reduce MVP cycles by 20-30%, while open-source AI frameworks cut development costs by 40-60% [19][21]. AlterSquare’s MVP Development program starts at $10,000, making it an accessible option for startups looking to integrate AI effectively.
"Starting small, focusing on solving a specific problem, and continuously iterating based on user feedback are crucial for successful AI integration in MVPs." – Panel of Industry Experts [21]
Tools and Methods for Building Context-Aware AI MVPs
Once you’ve ensured domain expertise, the next step is leveraging the right tools and strategies to build context-aware AI MVPs. These methods focus on training with relevant data, integrating external context, and rigorous testing.
Using Domain-Specific Data to Train AI
The quality of your AI model depends heavily on the data it’s trained on. Generic datasets lead to generic results, but domain-specific datasets enable your AI to address real-world problems effectively. Training models using paired text-task formats embeds domain knowledge into the system, allowing it to retain general capabilities while excelling in specialized areas. For instance, a 7B parameter model trained this way can perform on par with much larger models like BloombergGPT‘s 50B parameter model [25].
For industries dealing with sensitive data, such as healthcare or finance, synthetic data generation offers a solution. Techniques like Source2Synth create training data derived from authentic sources (e.g., tables, documents) while maintaining privacy. This approach has shown impressive gains, boosting performance by 25.51% for tabular question answering on WikiSQL and 22.57% for multi-hop question answering on HotpotQA [23]. Tools such as Tonic Textual and Tonic Structural specialize in free-text redaction, synthesis, and data masking, making them valuable for training AI models on sensitive datasets [24].
"Instead of predicting plausible text from training patterns, grounded models retrieve evidence from knowledge bases and cite their sources." – You.com Team [2]
Once your model is trained with domain-specific data, you can further enhance its capabilities by integrating external context through specialized APIs.
Pre-Built Tools and APIs for Adding Context
To add domain-specific context without costly retraining, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a go-to method. RAG allows your AI to connect to external knowledge bases or APIs in real-time, enabling it to retrieve and cite relevant information as needed [2][26]. Tools like vector databases store "embeddings" – numerical representations of domain data – allowing for semantic searches that inject precise context into responses [7][26]. While this approach may increase latency by 35-47%, it provides a balance between response speed and context depth [2].
A real-world example of this is Nubank, which used an AI tool called Devin to optimize a massive engineering project. Devin, fine-tuned on examples of manual migrations, helped the company break down a 6-million-line ETL repository into sub-modules. This resulted in an 8-12x efficiency gain in engineering hours and over 20x cost savings [27].
"Devin provided an easy way to reduce the number of engineering hours for the migration, in a way that was more stable and less prone to human error." – Jose Carlos Castro [27]
In customer-facing applications, platforms like Moveworks demonstrate the importance of context. By integrating internal data like employee directories, Moveworks ensures its conversational AI can distinguish between similar names, such as differentiating "Michael Jordan" the basketball legend from "Mike Jordan", an internal employee, providing accurate and relevant responses [7].
With the context integrated, the next crucial step is thorough testing to ensure the AI system performs accurately within its domain.
Testing AI Systems for Domain Accuracy
Testing begins with establishing a ground truth benchmark using verified Q&A pairs [28][22]. Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) play a critical role in defining what constitutes high-quality outputs and aligning these benchmarks with business goals. Even manually labeling 20 to 50 examples can provide a solid starting point for building a reliable evaluation framework [29].
Testing should cover a range of scenarios, including typical, negative, and edge cases, using high-capability models like GPT-4o. Regular human audits are essential for maintaining accuracy [22][28][29]. Pay close attention to citation accuracy – if it falls below 90%, it’s a sign that your retrieval system needs fine-tuning [2].
To systematically address errors, create a failure mode taxonomy that categorizes issues like hallucinations, retrieval errors, or formatting problems. Pivot tables can help prioritize fixes based on the frequency and impact of these errors [29]. Beyond technical metrics, connect evaluation results to business KPIs, such as cost per transaction or customer satisfaction, to clearly demonstrate the system’s value in practical terms [30].
Conclusion
What Startups Should Remember
AI without the right domain-specific data often produces irrelevant or misleading outputs. If your model lacks access to accurate, relevant information, even the most carefully crafted prompts won’t prevent errors or hallucinations [31].
For startups, the focus shouldn’t just be on prompts – it should shift to context engineering. This means designing a robust information environment filled with facts, constraints, and memory to guide the AI effectively [13][14]. Think of context as the backbone of your AI system, not just a collection of prompts.
To ensure reliable results, startups should prioritize three key strategies:
- Train AI with domain-specific data to enhance relevance.
- Use Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to integrate external, accurate context.
- Test outputs rigorously, aiming for citation accuracy above 90% [2].
Additionally, place critical instructions at the edges of prompts and review context elements that influence less than 95% of outputs to refine reliability [31]. These steps create a strong foundation for building AI products that are dependable and effective.
AlterSquare’s I.D.E.A.L. framework takes this a step further by embedding domain expertise throughout the entire AI development process. This approach minimizes risks like hallucinations or generic outputs, ensuring your AI-driven MVP is grounded in accurate, actionable knowledge from day one. By adopting these practices, startups can avoid the pitfalls that lead to failure in over 80% of AI projects [32].
FAQs
Why is domain-specific knowledge important for improving AI accuracy?
Domain-specific knowledge plays a key role in improving AI accuracy by providing essential context. This context ensures that AI models can generate outputs that are relevant and precise. Without it, models may misinterpret data, ignore critical details, or produce results that fail to meet practical needs. For instance, understanding industry-specific terminology or regulatory requirements allows AI systems to deliver outputs that are not only accurate but also actionable.
This is especially crucial in fields like healthcare or finance, where errors can have serious consequences. Incorporating domain expertise makes AI more reliable in these high-stakes areas. It also contributes to creating explainable AI systems, which helps users trust and verify decisions made by AI. When businesses ground their AI solutions in specific knowledge, they can ensure those solutions are both effective and aligned with their objectives.
What are AI hallucinations, and how can they be avoided?
AI hallucinations happen when generative AI models, like large language models (LLMs), produce information that sounds accurate but is actually false or completely made up. These errors occur because these models depend on patterns from their training data and may fill in missing details with incorrect information, especially if they lack enough knowledge or context in a specific area.
Reducing hallucinations requires anchoring AI responses in accurate, verifiable data. This can be achieved by using clear, domain-specific prompts, integrating reliable and up-to-date data sources, and building systems that ensure responses consider the right context. Focusing on these strategies helps businesses develop AI solutions that are more dependable and aligned with their objectives.
Why is Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) essential for improving AI accuracy?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) plays a key role in making AI outputs more accurate and dependable by merging the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) with reliable, external data sources. While LLMs are great at producing detailed and fluent responses, they can sometimes provide information that’s incorrect or outdated. RAG addresses this by retrieving relevant, up-to-date documents or data from trusted sources before crafting a response.
This method is particularly important in areas like law, finance, and technology, where accuracy and relevance are absolutely critical. By anchoring AI-generated outputs in verified, domain-specific information, RAG significantly reduces mistakes, limits hallucinations, and boosts reliability. In the end, it enables businesses to develop AI tools that are not only precise but also tailored to their unique objectives and the needs of their users.









Leave a Reply