AI is reshaping how businesses make decisions by enabling faster, data-driven actions. Instead of relying on slow, manual processes, AI systems now analyze massive datasets in seconds, propose solutions, and even execute decisions autonomously within set boundaries. This shift transforms enterprise software from static tools into dynamic ecosystems that can plan, act, and learn without human input.
Key takeaways:
- AI speeds up workflows by 30%-50% and reduces low-value tasks by 25%-40%.
- Autonomous decision-making follows a six-step loop: Sense, Propose, Compare, Choose, Act, Learn.
- AI-driven systems improve ERP and CRM cycles by 20%-30%, optimizing areas like pricing, inventory, and fraud detection.
- Decision Graphs and Intelligent Choice Architectures (ICAs) help AI map scenarios, evaluate trade-offs, and recommend actions.
- Predictive analytics and automated workflows boost efficiency, while recommendation systems simplify complex decisions.
AI’s role isn’t to replace humans but to handle repetitive tasks and high-pressure scenarios, allowing teams to focus on strategic and ethical decisions. Companies that integrate AI effectively report better outcomes, including faster processes, higher profit margins, and improved customer experiences. However, success depends on robust governance, clear business goals, and measurable metrics.
How Decision Intelligence & AI Agents Are Redefining Enterprise Operations
sbb-itb-51b9a02
AI-Powered Decision Intelligence: A New Approach
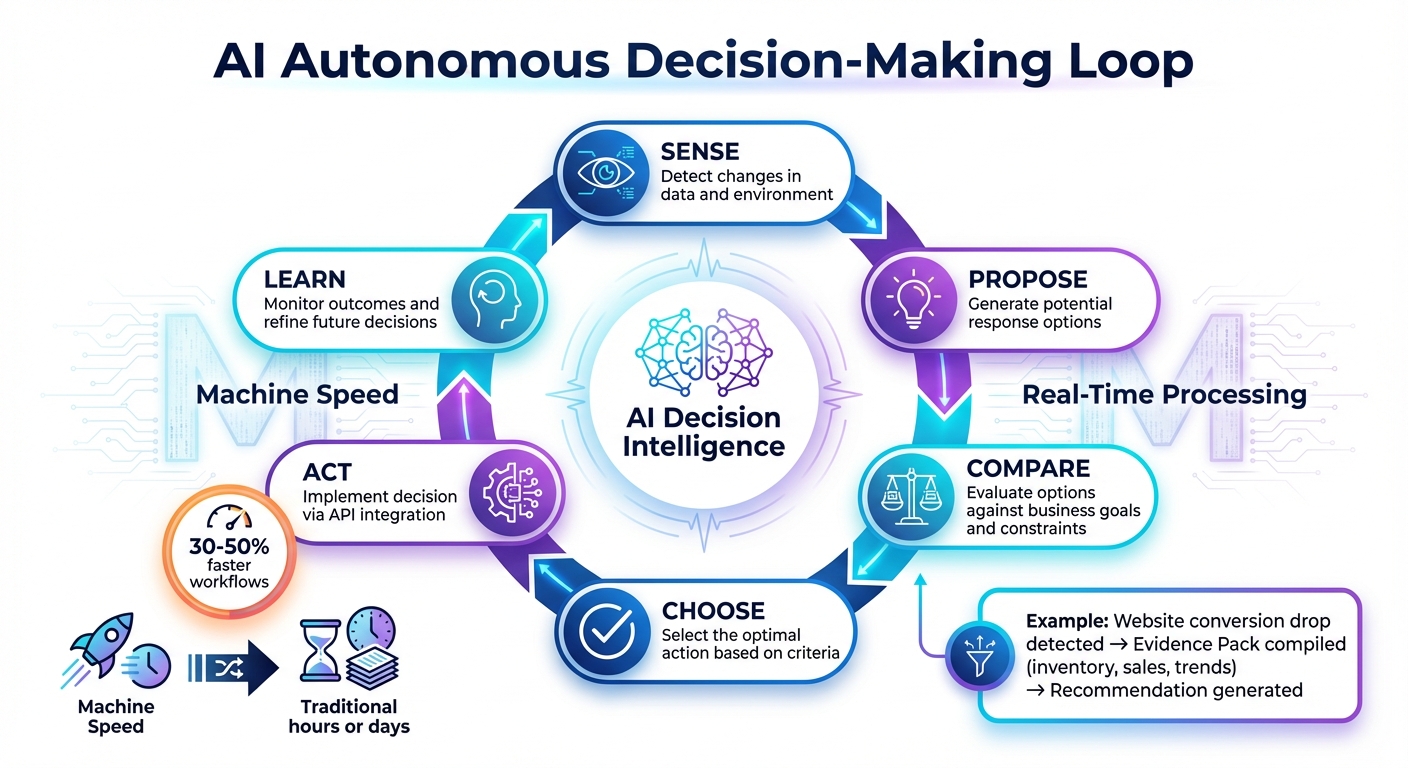
AI Six-Step Autonomous Decision-Making Loop in Enterprise Systems
Traditional decision-making often follows a predictable, time-consuming path: gather reports, analyze data in meetings, debate options, and eventually decide. This process can stretch over hours or days, and by the time a decision is made, the situation may have shifted. AI-powered decision intelligence changes the game entirely. It operates at machine speed using a six-step autonomous loop: Sense (detect changes), Propose (generate responses), Compare (evaluate against goals), Choose (select the best option), Act (implement via API), and Learn (monitor outcomes) [7].
But it’s not just about speed. AI reshapes how decisions are made. Monica Caldas, Global CIO at Liberty Mutual Insurance, put it well:
"We realized we needed to shift the mindset from building models to engineering decisions" [2].
This shift means focusing less on perfecting algorithms and more on creating the right decision framework – defining available choices, applying constraints, and evaluating trade-offs. AI systems now rely on Decision Graphs, which map out business scenarios, potential actions, and constraints like budget limits or compliance rules. Think of it as a GPS for decision-making. For instance, if AI detects a sudden drop in website conversions, it compiles an Evidence Pack with key data like inventory levels, sales forecasts, and historical trends to back up its recommendations [7].
How AI Improves Data-Driven Decisions
Today’s enterprises face data volumes that far exceed human capacity to process. A large grocery store, for example, manages 50,000 unique SKUs, while major airlines oversee over 100,000 flights each month [6]. Manually managing these variables – whether adjusting prices or allocating resources – is simply not feasible. AI, however, can optimize these complexities in real time.
What sets AI apart is its ability to create Intelligent Choice Architectures (ICAs) – decision frameworks that present multiple viable options, each with clear trade-offs. These ICAs reveal opportunities hidden within massive datasets [8][2]. Companies that utilize AI to build these advanced decision frameworks achieve better results across various industries [8]. The difference lies in AI’s ability to process complex patterns and logical inferences that humans can’t easily identify. It uncovers relationships and causality that would otherwise go unnoticed [9][6]. Funmi Williamson, Chief Customer Officer at Southern California Edison, shared how her team shifted their perspective:
"We stopped asking, ‘What can AI do?’ and started asking, ‘What choices are we making badly?’" [2].
This approach helps organizations pinpoint where AI can make the biggest difference. Research indicates that poor or delayed decision-making costs companies nearly 3% of their profits – equivalent to $150 million for a $5 billion business [9]. AI bridges this gap by processing data instantly and executing decisions far faster than traditional human review cycles.
By leveraging these dynamic decision frameworks, machine learning takes enterprise systems to the next level.
Machine Learning in Enterprise Systems
Machine learning turns static systems into adaptive, self-improving ones. Unlike rigid automation, ML models refine their logic by learning from outcomes [1][7]. This creates a natural extension of the six-step autonomous loop, continuously enhancing decision-making processes.
AI proves especially effective in high-pressure scenarios. For example, during Black Friday, AI manages thousands of simultaneous micro-decisions across server capacity, pricing, and inventory [7]. While humans rely on theories and heuristics that can be biased or inconsistent, AI uses advanced pattern recognition to navigate complexities beyond human cognitive limits [6].
Philippe Rambach, Senior VP and Chief AI Officer at Schneider Electric, explains this transformation:
"AI doesn’t replace decision-making – it reframes what decisions are worth making by humans" [2].
This reframing is pivotal. As ML models grow more advanced, they take on routine operational decisions, allowing human teams to concentrate on strategic choices that require creativity, empathy, or ethical consideration. The result is a collaborative intelligence model where AI handles speed, precision, and pattern analysis, while humans bring context, values, and nuanced judgment to the table. Together, they form a powerful partnership for navigating today’s complex business challenges.
AI Applications in Enterprise Software
AI’s role in reshaping enterprise systems is undeniable, with practical applications that are changing how businesses operate. Three standout uses include predictive analytics for forward-looking planning, automated workflows to eliminate redundant tasks, and intelligent recommendation systems that enhance decision-making. Each of these targets a unique aspect of enterprise functionality, driving efficiency and innovation.
Predictive Analytics for Better Planning
Relying solely on historical data for planning is like driving while looking in the rearview mirror – it works, but it’s not ideal. Predictive analytics changes the game by integrating external signals to anticipate market trends before they occur. This proactive approach allows businesses to stay ahead of the curve rather than reacting to events as they happen.
The numbers back up its impact. AI’s capabilities are doubling in price-performance every three months [10], enabling businesses to embrace what’s called the "micro-market paradigm." This shift moves companies from broad mass-market strategies to highly personalized, scalable targeting [10]. Take the U.S. wellness market as an example: currently valued at $700 billion, it’s projected to grow past $5 trillion by 2040 [10].
Modern predictive systems go beyond just forecasting – they employ causal inference to identify the "why" behind trends. AI has evolved to include reasoning and orchestration, meaning it doesn’t just predict the future but can recommend and even execute specific actions autonomously within set boundaries [1][10]. The focus here isn’t just efficiency (doing things right) but effectiveness (doing the right things) [10].
While predictive analytics helps businesses plan smarter, automated workflows ensure those plans are executed efficiently.
Automated Workflows for Higher Efficiency
AI-driven workflows take automation to the next level. Unlike traditional systems that follow rigid scripts, AI workflows adapt to changing conditions and unexpected challenges. Businesses that have adopted these workflows report significant gains – processes are sped up by 30% to 50% [4].
In practical terms, AI has reduced manual workloads in IT and HR operations by up to 60%, while insurance companies using AI-driven case management have cut claims processing times by 40% [4]. Another major benefit is 24/7 operational continuity. AI can handle sudden spikes in data traffic without requiring extra staff and can even work with outdated systems by mimicking human interactions [4][7].
However, implementing these systems isn’t without challenges. Multi-step workflows face what’s known as a "reliability cliff." For instance, if each step in a five-step process has 90% accuracy, the overall success rate drops to just 59% [3]. The solution? Start simple. Alex Strick van Linschoten from Vanishing Gradients advises:
"If you can get away with not having something which is fully or semi-autonomous, then you really should and it’ll be much easier to debug and evaluate and improve" [3].
A hybrid approach often works best. In DevOps, for example, using rules for 77% of incidents and reserving AI for complex cases can save up to $80,400 annually compared to AI-only systems [3]. The key is combining deterministic rules for straightforward tasks with AI for more nuanced scenarios, and always including human oversight for high-stakes actions like large financial transactions [4][7].
Intelligent Recommendations for Better User Experience
Recommendation systems in enterprise software are evolving beyond merely suggesting options – they’re reshaping how decisions are made. These systems, often referred to as Intelligent Choice Architectures (ICAs), combine tools like scenario optimization, neural networks, and generative AI to present recommendations in clear, understandable terms [2][12].
The impact on business performance is striking. Research shows a 95% correlation between a company’s decision-making quality and its financial performance [12]. Companies that mentioned AI during investor calls in 2023 saw their stock prices rise by an average of 4.6%, compared to 2.4% for those that didn’t [12]. Additionally, 89% of organizations believe AI will drive revenue growth, improve efficiency, and enhance customer experiences [11].
One of the biggest strengths of modern recommendation systems is their ability to reduce cognitive load. Instead of requiring employees to sift through mountains of data, AI handles the heavy lifting, allowing teams to focus on interpreting insights and making strategic decisions [2][12].
This division of labor reimagines decision-making. Routine, operational choices are delegated to AI, while humans focus on areas requiring creativity, empathy, or ethical judgment [2]. The result is a powerful partnership – AI brings speed and pattern recognition, while humans contribute context and values, creating a balanced and effective decision-making framework.
Implementing AI Decision Systems: What to Consider
To successfully implement AI systems, organizations need strong architecture, governance, and alignment with their strategic goals. Skipping these basics often leads to "pilot purgatory", where projects stall before delivering meaningful results. It’s worth noting that 70% to 85% of Generative AI initiatives fail to hit ROI targets, mainly due to governance issues rather than technical shortcomings [18].
Building AI-Ready Enterprise Architectures
A functional AI system relies on a seven-layer stack designed to transform raw data into reliable decisions. At its base is the data input and preprocessing layer, which organizes data from warehouses and APIs, capturing metadata and lineage during ingestion [13]. Moving up, the semantic layer converts business terms into machine-readable formats, reducing errors caused by ambiguous language [13][14].
The middle layers handle critical operations. A prompt engineering pipeline manages templates and token limits, while the model orchestration layer directs tasks to the most suitable model based on factors like cost, speed, and security [13]. Think of this layer as an air traffic controller, deciding whether to use a costly large language model or a smaller, faster alternative depending on the task.
For example, in 2025, migrating a React 19 microservice to an AI-enhanced CI/CD pipeline using tools like Argo Rollouts and Kubernetes led to a 25% reduction in lead time, a 28% increase in deployment frequency, and a 26% improvement in MTTR [16].
A well-designed architecture also supports gradual autonomy. Start with AI agents that make recommendations requiring human approval, then scale up to systems capable of full autonomy with safeguards like kill-switches [16]. As GoodData explains:
"If your AI system can’t explain how it arrived at a result, it can’t be trusted. And if it can’t be trusted, it can’t scale" [13].
To ensure scalability and compliance, include a model gateway for centralized inference requests and optimize data management with lakehouses or AI-ready data fabrics [14][15]. Treating data as a product is essential before scaling AI systems.
Once the architecture is in place, a robust governance framework becomes the backbone of ethical and efficient AI deployment.
Governance and Ethical AI Practices
AI governance isn’t just an upgraded version of traditional data governance – it’s a whole new approach. Unlike static datasets, AI models evolve after deployment, making thousands of decisions every second [18]. This speed often outpaces human review, and 40% of technology executives admit their governance programs fall short [17].
The risks are real. Systems without governance are 40% more likely to show bias and can increase operational costs by up to 30% due to inefficiencies and compliance failures [19]. A stark example comes from the Dutch government: between 2019 and 2021, its algorithmic system for detecting child benefit fraud wrongfully targeted minority families, leading to the government’s resignation in January 2021 [18].
Effective governance requires a multi-layered framework that covers organization, legal compliance, ethics, data operations, and security [17][19]. Address potential issues early by embedding automated checks into CI/CD pipelines to block non-compliant models from deployment [18].
Classify AI applications into risk tiers – low-risk tools may need only monthly reviews, while critical systems like credit scoring require daily oversight and committee approvals [18]. For high-stakes decisions, assign "Judgment Holders" to ensure human oversight remains a priority [20].
By prioritizing transparency, trust, and security, organizations can boost AI adoption and user acceptance by 50% by 2026 [17]. As Databricks states:
"Governance defines how decisions are made about AI development and use… together, governance and security form the foundation for safe, scalable AI" [17].
With governance in place, the next step is ensuring AI aligns with measurable business objectives.
Aligning AI with Business Goals
A common pitfall in AI implementation is focusing on technology without a clear business problem in mind. The most successful initiatives take the opposite approach – tying each use case to a specific business goal, such as reducing costs, improving speed, enhancing quality, or elevating customer experience [22].
The BXT Framework (Business, Experience, Technology) offers a practical way to structure AI projects. Define the business objective, outline the desired user experience, and establish measurable success metrics [21][22].
For instance, 61% of enterprise leaders prioritize AI for IT service management tasks like ticket triage, while 40% focus on data workflows such as cleaning and categorization [15]. These areas are chosen for their potential to deliver quick, measurable impact.
To start, use ready-made SaaS tools like Microsoft 365 Copilot for faster results before moving to custom development platforms [21][22]. As Tray.ai puts it:
"Integration is the challenge to solve. Think of LLMs like new appliances. The magic only happens once they’re connected to power and plumbing" [15].
Establish an AI Cloud Center of Excellence to centralize governance, monitor regulations, and ensure accountability for AI outcomes [22]. This team can rank AI use cases by their impact, feasibility, and desirability to avoid wasting resources [21]. Keep in mind that AI systems are only as effective as the data they rely on – ensure your data is fresh and accessible before attempting to scale [15].
Measuring AI Impact on Enterprise Decisions
Once AI systems are up and running, proving their value becomes a challenge. Traditional ROI calculations often fall short because AI’s influence goes beyond basic cost savings. For instance, 85% of organizations increased their AI investment in 2024–2025, yet only 6% reported payback within the first year [24]. Most companies find it takes two to four years to realize the expected ROI – much longer than the typical 7 to 12 months for standard tech investments [24].
Initial AI pilots often delivered returns of 31%, but as projects scale, the ROI tends to stabilize at around 7%, which is below the typical 10% cost of capital hurdle rate [26]. However, the top 10% of organizations achieve an average ROI of 18% by focusing on the right metrics and use cases [26].
Key Metrics for AI Success
Measuring AI performance requires a shift from static metrics to adaptive ones that reflect how decision-making improves over time. Organizations that use AI-driven KPIs are 5 times more likely to align their incentives with business goals compared to those relying on outdated metrics [23]. This approach emphasizes tracking how AI enhances decision quality, aligning with Intelligent Choice Architectures by continuously refining decisions based on real-time data.
The process begins with establishing baseline performance metrics before implementing AI [25]. From there, organizations can measure improvements across several dimensions:
- Efficiency metrics: Track tangible outcomes like reduced processing times and fewer manual tasks.
- Financial metrics: Measure increases in operating profit and revenue per transaction, which can improve by 10% to 30% in optimized deployments [25][26].
- For autonomous AI agents, monitor KPIs like agent-to-human handoff rates (how often human intervention is needed), reasoning coherence scores (decision quality), and decision accuracy rates (correctness over time) [5].
Monica Caldas, Global CIO at Liberty Mutual Insurance, captures this mindset shift: "We realized we needed to shift the mindset from building models to engineering decisions" [2].
It’s also important to consider intangible benefits. For example, stronger vendor relationships and improved employee satisfaction can deliver value that’s harder to measure but just as impactful [24]. Reflecting this broader perspective, 64% of AI budgets now focus on core business areas like supply chain, finance, and R&D rather than peripheral activities [26].
| Metric Category | KPIs |
|---|---|
| Efficiency | Processing time reduction, error rate decrease, manual task elimination [25] |
| Financial | Operating profit improvement, revenue per transaction, deal size growth (10–30%) [25][26] |
| Agentic AI | Agent-to-human handoff rates, reasoning coherence, decision accuracy [5] |
| Strategic | Option innovation rate, framing agility, feedback loop integration speed [2] |
Examples of AI-Driven Transformation
These metrics translate into real-world business improvements, as demonstrated by leading organizations:
- Nestlé replaced manual expense management processes, achieving a 3x increase in employee efficiency for report creation [25].
- SA Power Networks boosted infrastructure reliability with a 99% success rate in identifying poles likely to corrode, saving $1 million annually [25].
- Microsoft streamlined supply chain planning, cutting manual processes by 50% and improving on-time planning by 75% [25].
- Chobani reduced administrative workloads by 75%, focusing on time savings and employee satisfaction [25].
Each of these organizations started with clear, measurable goals and tracked KPIs tied directly to business outcomes.
Funmi Williamson, Chief Customer Officer at Southern California Edison, emphasizes this shift in focus: "We stopped asking, ‘What can AI do?’ and started asking, ‘What choices are we making badly?’" [2].
This change in perspective is crucial for accurately measuring AI’s impact.
Conclusion
AI is revolutionizing enterprise decision-making, moving beyond static, rule-based systems to dynamic, autonomous processes. This evolution means AI is no longer just about generating insights – it’s about actively driving decisions that deliver measurable results.
To succeed in this new landscape, businesses need to rethink their operating models. This includes redefining KPIs, setting clear decision-making boundaries, and ensuring strong governance structures. Notably, 78% of C-suite executives believe that unlocking the potential of AI-driven agents requires entirely new ways of operating [5]. As discussed in the context of AI-powered decision intelligence, these models must strike a balance – allowing AI the autonomy to act while maintaining human oversight and adaptability.
"The next phase of enterprise evolution is the rise of AI agents… which will extend AI’s reach beyond analysis to reasoning and orchestration – enabling systems that can plan, decide, and act within defined parameters."
Organizations leading in AI adoption are seeing remarkable results. Companies that excel in integrating AI are 32 times more likely to achieve top-tier business performance [5]. And by 2027, 67% of executives anticipate AI agents will take independent action within their organizations, a significant jump from today’s 24% [5].
AlterSquare is here to guide businesses through this transformation. Whether you’re launching your first AI feature or overhauling your decision-making framework, their tailored solutions are designed to deliver measurable outcomes. With experienced engineers by your side, you can accelerate progress while reducing risks, ensuring your enterprise evolves to meet modern demands effectively.
FAQs
Where should we start with AI decision-making in ERP or CRM?
To get started, take a close look at your data and processes. Evaluate your existing systems to pinpoint where AI can make a difference – think predictive analytics or automating repetitive tasks. Prioritize data quality and ensure your systems are ready for integration.
It’s also important to build AI knowledge within your teams. Educate them on how AI works and its potential impact. From there, create a clear strategy and start with small-scale pilot projects. These pilots allow you to test and fine-tune models without causing major disruptions.
This step-by-step approach helps AI seamlessly improve decision-making, especially in ERP and CRM systems.
How can we establish safe boundaries for autonomous AI actions?
To ensure safe boundaries for autonomous AI, it’s important to use a structured autonomy framework. This framework defines different levels of AI behavior, ranging from simple automation to complete autonomy. Alongside this, implement governance tools such as predefined rules, oversight protocols, and audit-grade evidence. These measures are essential for maintaining safety and transparency.
By setting these guardrails, organizations can better manage risks, uphold accountability, and ensure that AI actions align with established standards. This approach also minimizes uncertainty, creating a more controlled and reliable AI environment.
What KPIs best prove AI is improving decision quality?
Key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect AI’s role in improving decision-making are those that offer predictive insights, adapt to changing conditions, and align closely with an organization’s strategic objectives. These AI-driven metrics excel at delivering real-time insights, forecasting trends, and monitoring areas like operational efficiency, profitability, and growth.
By leveraging predictive analytics and automating routine workflows, these KPIs minimize human error, enhance organizational flexibility, and empower teams to make smarter, faster decisions. They also provide a clearer way to measure progress toward specific goals, ensuring that businesses stay on track and responsive to evolving needs.









Leave a Reply